 | 2 comments
| 2 comments
Lay summary and illustrations by Yasi Yaghoub
Edited by Crystal Han
This summary is based on the original paper by ICORD researcher Dr. Bonita Sawatzky and her colleagues Celine Edwards, Annemarie Walters-Shumka, Shira Standfield, Tamara Shenkier, and Susan Harris. Read the original paper here.
Why is this study important?

Aging women are likely to experience breast cancer and spinal cord injury (SCI) simultaneously. Despite the improvements in the treatment processes, breast cancer treatment can leave women with SCI with health complications that can affect their quality of life.
What is the objective of the study?
The goal of this study is to improve healthcare workers’ understanding of the correlation between breast cancer, to help create the best course of treatment. SCI This study focused on two main points:
- To provide knowledge regarding the consequences of breast cancer treatments on the health of women with SCI
- To encourage researchers to investigate the breast cancer treatment-related health outcomes
Health conditions associated with breast cancer treatment in women with SCI:
Limitations to Shoulder Mobility
Having adequate shoulder mobility for individuals with SCI, 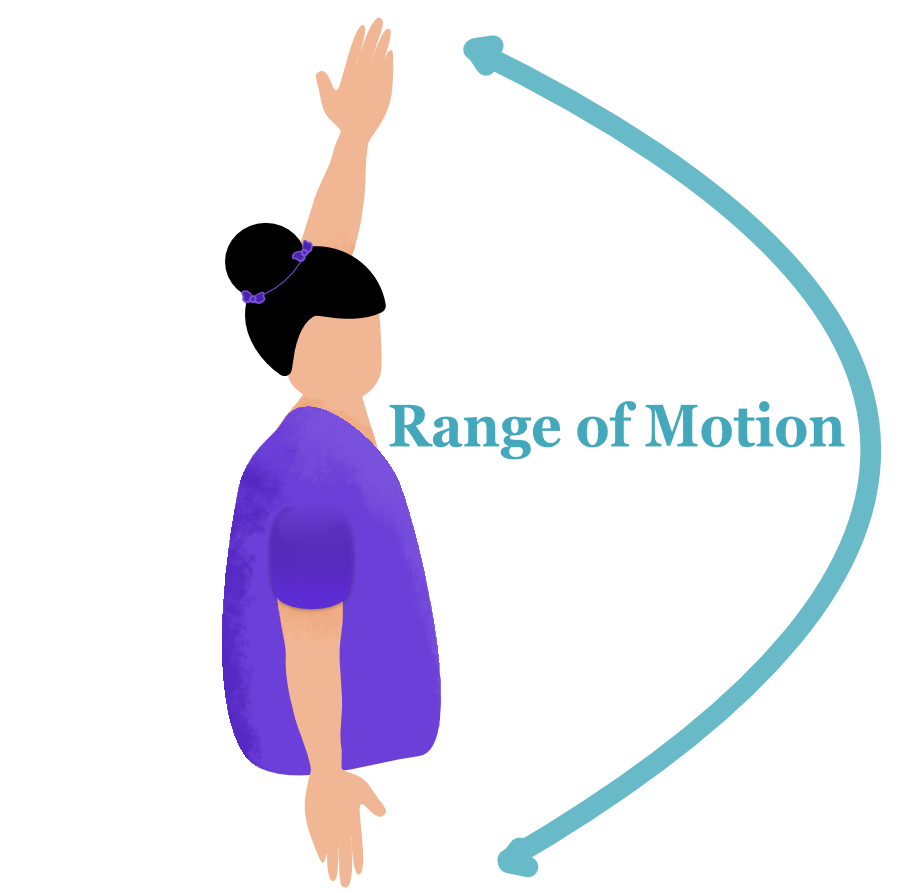 especially for manual wheelchair users, is important as it allows them to reach from a seated position. Full shoulder range of movement (ROM) is critical for propelling the wheelchair and can be associated with better overall life quality.
especially for manual wheelchair users, is important as it allows them to reach from a seated position. Full shoulder range of movement (ROM) is critical for propelling the wheelchair and can be associated with better overall life quality.
Breast cancer treatment, however, can lead to shoulder movement restriction and upper limb weakness, which in turn, limits the ROM. Radiation treatment can also result in muscle weakness, which in turn, can affect the strength and mobility of the shoulders.
These factors should be taken into consideration when deciding to proceed with radiation treatment for breast cancer patients with individuals with SCI.
Lymphedema
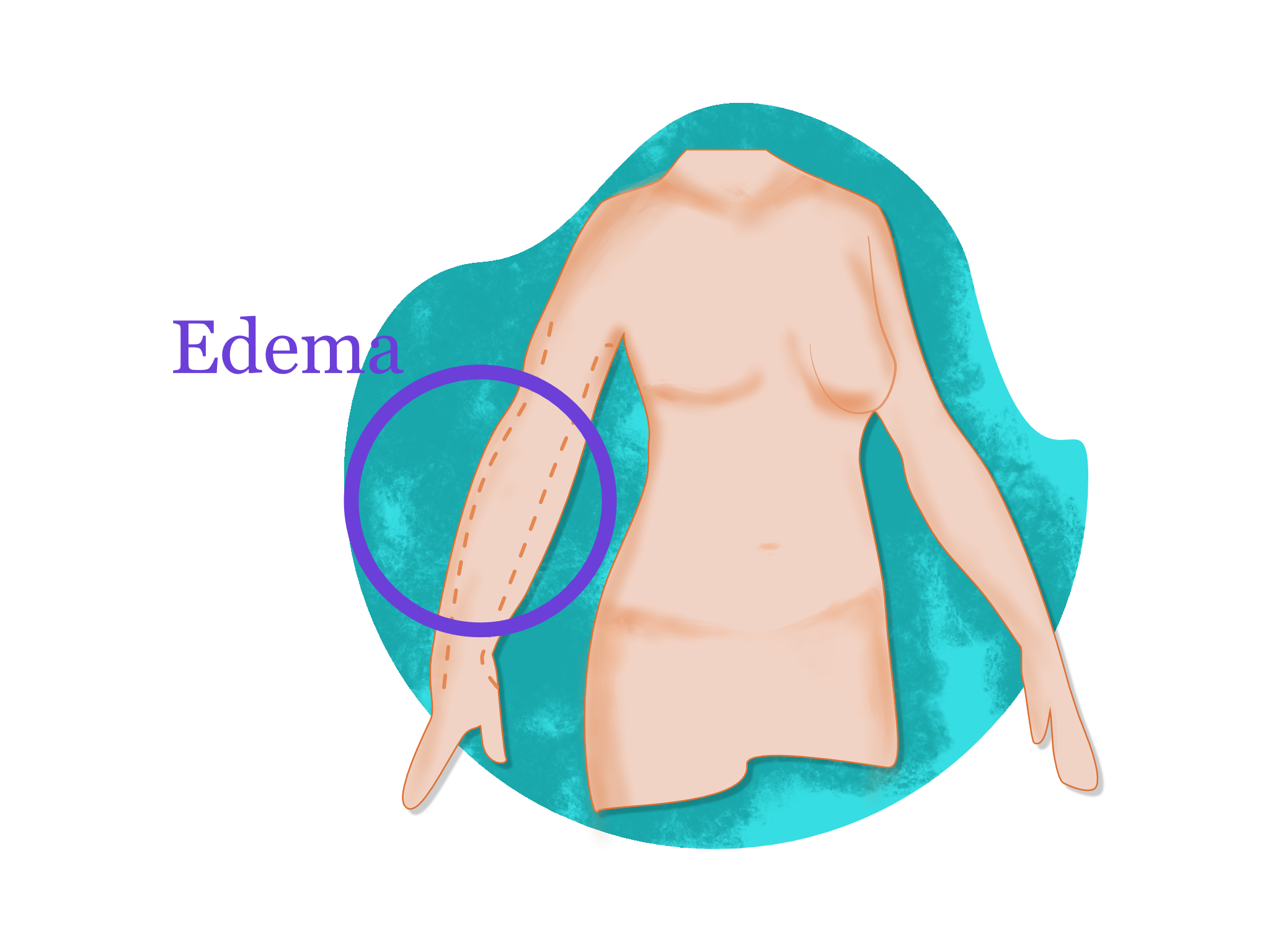 Edema is the build-up of excessive body fluid in regions of the body, causing swelling. A more specific type of edema, called lymphedema, is a condition in which a fluid in our body known as lymph builds up in areas of the body where it should not be, and causes swelling. This condition is commonly caused by cancer treatments and can impact an individual’s ability to complete daily routines.
Edema is the build-up of excessive body fluid in regions of the body, causing swelling. A more specific type of edema, called lymphedema, is a condition in which a fluid in our body known as lymph builds up in areas of the body where it should not be, and causes swelling. This condition is commonly caused by cancer treatments and can impact an individual’s ability to complete daily routines.
- Lymphedema in women with SCI increases the burden associated with SCI, which in turn, impacts their daily routines.
- Healthcare professionals should attentively perform skin inspection, particularly at the underarm areas, to catch lymphedema at early stages.
Wound care nurses may provide skincare education to SCI patients, especially if lymphedema occurs. This is particularly important for those with higher-level spinal cord damage and greater areas of reduced sensation.
Pain: 
- Chronic pain can be caused by the treatment and/or cancer itself. The majority of Individuals who undergo breast cancer treatment, report arm and breast pain 24 months after the treatment. To reduce the treatment-related side effects and the recurrence of cancer, physical activity is essential for the patients.
- 30% of the Individuals with SCI, however, experience persistent shoulder pain due to increased demand on shoulder joints.
- This persistent pain limits their ability to exercise and achieve a healthy lifestyle. Greater pain intensity is associated with lower perceived self-health.
- During breast cancer treatment, patients are often administered medicine that increases muscle and joint pain.
- Continuous pain management is essential for individuals with SCI.
Fatigue
- Cancer-related fatigue is different from other manifestations of fatigue as it has a greater severity, longer duration, and is not resolved with resting. Fatigue is often associated with symptoms such as pain, sleep disturbance, depression, and mental health complications. Fatigue can also reduce individuals’ involvement in personal and social activity, thus affecting their quality of life.
- Women with SCI mostly rely on the strength of their upper extremity to move, therefore, fatigue can force them to transition from manual wheelchairs to powered wheelchairs.
Adding fatigue caused by breast cancer treatment to an already traumatic event, such as SCI, can increase mental health and physical challenges women face.
Bladder and bowel health
Individuals with SCI are at risk of bladder and bowel dysfunction.
- It is important for healthcare workers to enable patients to remove the triggers of full bladders by having them seated upright.
- Oncologists and patients should be aware of the fact that chemotherapy can exacerbate bladder dysfunction.
Skincare
Radiation therapy can impact skincare in individuals with SCI.
- Accurate positioning and maintaining that position on the radiation table are important throughout the session. Therapists and family members can manually assist the patients to achieve that position.
- Long chemotherapy duration also increases the risk of wound and pressure sores development. Women with SCI are particularly prone to this issue due to steroid use, malnutrition, suppression of the bone marrow, and sweating below the level of injury.
Immune suppression
- Immune suppression occurs when the immune system’s ability to fight infections is compromised.
- Individuals with SCI have a weak immune system as a consequence of this condition, making them more susceptible to infections, which healthy individuals are able to fight off easily.
Breast cancer treatments such as chemotherapy can further worsen the state of the immune system, making individuals recovering from SCI and breast cancer, more susceptible to other infections.
Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis is a disease that weakens the bones, increasing the chance of sudden bone fracture in individuals.
- Chemotherapy can lead to conditions such as ovarian failure, which in turn, can contribute to bone loss in women undergoing the treatment.
- Bone mineral density should be closely monitored for women with SCI and breast cancer, especially those who undergo chemotherapy.

